I discussed cold welding metal with a neighbor, and my grandson overheard the conversation. He’s familiar with welding, but cold welding was new to him, which prompted a couple of questions, what is it used for, and how does it work without heat.
Cold welding is a process that creates unions between metal pieces by removing impurities and oxygen from their surfaces in vacuums, then pressing these metals together without fusion or heat. The pressed-together surfaces form a bond called cold welded joints.
Words like “cold” and “welding” just don’t seem to go together. However, they do work well together, and for some welding applications, it works better than standard welding. In this article, I explain how cold welding works and its uses.
Contents
How Cold welding works:
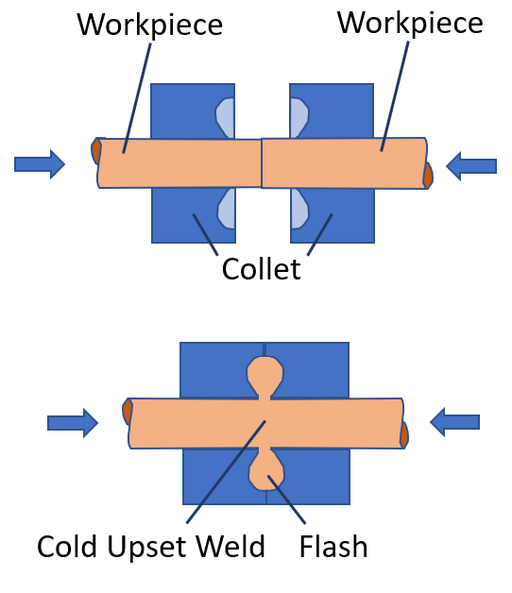
When two similar metal surfaces come in contact, the electrostatic force of atoms attracts. The air around a metal is like armor that guards it against being welded. Without the protection of oxygen, surfaces would combine and join as one without any resistance.
But in normal conditions, they don’t join because of the impurities and oxygen between them. Metal surfaces typically react with atmospheric oxygen to form oxides, which create a barrier.
To get around this, you must clean the surface and create a vacuum to remove oxygen from between the surface of metals. The metal pieces will fuse and form a cold weld with the impurities and oxygen out of the way.
Types of Cold Welding:
Cold welding is a process where two pieces of metal are welded together without heat. The difference between different types of cold welders can be confusing, but it all comes down to how they work and what material you are using for your project.
A cold weld occurs at room temperature. However, there are a few different processes that can be considered “cold welding,” and they all differ in the way they work. Here are some cold welding methods.
Contact Welding
Contact welding is another phrase used to describe cold welding. It is the basic process we mentioned above. In it, metal surfaces are first freed from the oxide layer then clean metal plates can be bonded by pressing together manually or by machines. To get the best results, it is often done under low pressure.
Tig Pulse Welding
It is basically a tig welder with a cold setting and is used to spot weld thin metal. Most TIG machines that cold weld also has a setting to weld in hot mode. The way it works is to send a high current pulse for micro or milliseconds, which is enough to bond thin or soft metals. (e.g., aluminum)
Cold Metal Transfer Welding
Cold metal transfer welding is a type of MIG welding typically performed by a robot. Instead of using electricity to produce a continuous arc, as in standard MIG welding, it uses short-circuiting breaks to melt the welding wire into droplets, emitting less heat than traditional MIG machines.
Advantages of Cold Welding
Cold welding allows you to bond thin, delicate metals like aluminum and gold that would be impossible to weld using standard welding processes. It is also valuable for use in heat-sensitive areas.
It is a quick way to produce a strong weld while bond strength is almost equal to its parent metals. It’s like forming a new metal piece. Even wires of about 0.5mm diameter can be welded by this method. Cold welding is typically the best option for welding different types of wires and thin metals together.
Uses of Cold Welding:
Cold welding is the perfect technique for ensuring that your wires are perfectly joined together. You can perform this method quickly and without heat; it’s primarily used with aluminum, copper, and brass.
It’s frequently used in the aerospace and auto industry. Cold welding is also an excellent method to use when making jewelry or working with stainless steel because it won’t deform or discolor the metal.
Here is a list of the most common uses for cold welding:
- Weld wires, as it creates a perfect weld.
- Welding metals like aluminum, copper, silver, and gold
- Automobile industries for welding sheet metals.
- Used to make heat-sensitive electrical components (like semiconductors).
- Used to seal heat-sensitive containers containing explosives e.t.c.
Limitations of Cold Welding:
Cold Welding can be a great way to join metal, especially in the absence of other options. However, there are some limitations you need to consider before implementation:
- The welding surface needs to be flat without any roughness for best results.
- Metal surfaces should be free of impurities and oxide layers to form a strong weld.
- Oxide layers on the metal surfaces are ofen difficult to remove.
- It lacks penetration power, so the majority of bond strength depends on weld surfaces.
- It is only good for welding non-ferrous metals.
- It is difficult to gauge the strength of the weld.
Are Tig welding and cold welding the same?
Standard TIG welding is not “cold welding.” However, there are TIG machines that have a cold welding option. These machines used for cold welding don’t follow the concept of contact welding.
But they are called cold welders because they emit less heat, or their weld can quickly absorb heat, and you can touch the surface immediately after welding. DC or AC Tig welders with a spot welding function are performed slowly to avoid generating much heat.
It uses a quick current spark to weld metals, the current pulse is passed for a short duration, but it is enough to weld thin or metals. These TIG welders are commonly used to fill holes or remove defects from a metal surface.
Cold welding vs Hot welding
It’s like comparing standard coffee to cold coffee; one is hot while the other is not. Similarly, the main difference between these two welding methods is heat emission.
One joins metal parts under pressure using electrostatic force or welding through a current pulse. While the other uses heat to melt and combine metal parts.
In hot welding, a substantial amount of heat is provided, resulting in metal pieces being melted and fused when cooled; also, electrode wire is fed in some conditions. In cold welding, either vacuum or high pulse current is used to join metals.
Cold Welding makes a clean weld with a bond strength almost equal to their parent metals. While hot welding often produces slag or weld layer, which is ground down to create a smooth, strong bond.
Can you make a cold welding machine?
You can find DIY videos about anything on the internet in today’s world. There are several videos on how to make different welders at home, but I couldn’t find a way to make a cold welder.
However, you can weld metals by contact method using a vacuum box or bag. Here is a video to help you out.
Are Cold welders cheap?
Doing contact welding under pressure or vacuum is cheap but hard to perform. In contrast, cold spot welding is done by Tig pulse cold welding machines. They vary in prices depending on the company and features:
Here are two cold welding machines sold on Amazon:
- 【Function】TIG, PULSE, COLD, CLEAN, Auto and Au-Ag welding
Prices pulled from the Amazon Product Advertising API on:
Product prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.
Be aware that this machine is designed to work with European 220 circuitry. If you’re in the U.S., check with the manufacturer or an electrician to determine what you need to do to set it up here.
- 【Function】This is a cold welding/aluminum welding machine with a voltage of 220V. The current is 200 AMP. There are 4 modes at the same time: pulse TIG, HF TIG, cold pulse, cold welding, suitable for aluminum, stainless steel and thinner metals.
Prices pulled from the Amazon Product Advertising API on:
Product prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.


